Toxins are linked to many health concerns. One of the things I test for in my patients is the presence of toxins. When toxins like lead or cadmium are found we try to determine the root cause – where is it coming from? One of the first things we look at is the source of drinking water.
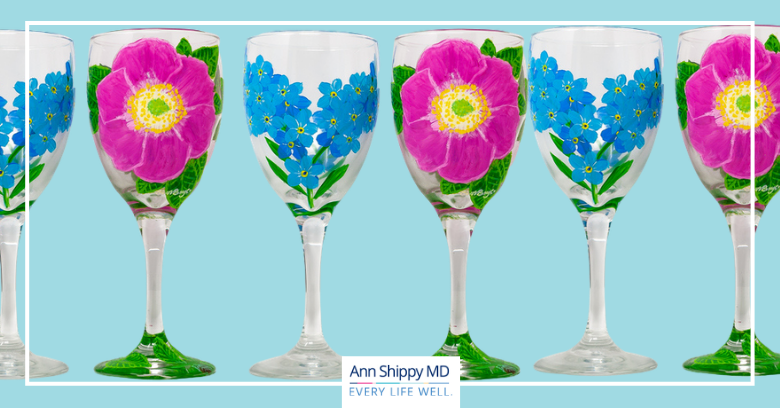
Using a good water filtration system is one way to lower lead exposure. But what happens when the lead is coming from the drinking glass, and not what’s inside? Well, that can happen when you drink from decorative glassware. Yup, the cute glassware from the trip to the amusement park, or the fun novelty glass with your kid’s favorite superhero painted on the side could be poisoning you and your family.
Researchers from the University of Plymouth analyzed drinking wear, by testing 72 new and used decorated tumblers, beer and wine glasses and jars. They tested them for lead and for an even more toxic metal, cadmium. First discovered in Germany in 1817, cadmium has been used as a pigment for years because of its ability to produce brilliant yellow, orange, and red colors. Results of the study revealed that lead was found in glasses that came in a variety of colors and gold-leaf designs. Cadmium concentrations were highest in glassware with red enamel. When ingested these metals are highly toxic, especially to children.
Cadmium is an endocrine disrupting chemical (EDC) linked to developmental disruptions with children. Harvard researchers reported that children who tested positive for high levels of cadmium are three times more likely to have learning disabilities. In India, researchers reported that early-life low-level cadmium exposure was associated with lower intelligence scores among children.
Dr. Bruce Lanphear, a pediatrician and epidemiologist at Simon Fraser University is a leading expert on lead toxicity in children. In a piece about lead toxicity in glassware, he told Scientific American that “the pattern we’re seeing here with cadmium is very consistent with what we see with other toxicants,” including lead and mercury.
Lead functions a lot like cadmium. It’s also an EDC with fatal consequences when there’s chronic exposure. Among adults cadmium can trigger neurological problems. Lead in adults increases symptoms of high blood pressure, joint and muscle pain, headaches, mood disorders and many other ailments that can disrupt the quality of life.
Kids under 6 years old are especially susceptible to lead poisoning. Like cadmium it leads to developmental problems both mental and physical. Reconsider whether to use glassware made specifically for children with the cartoons, superheroes or movie characters painted on them. In 2010, the Associated Press commissioned a lab analysis of children’s drinking glasses that were made in China and sold at a Warner Brothers Studios store.
Tests results showed that children’s drinking glasses exceeded federal limits for lead in children’s products by up to 1,000 times. They found even higher doses for cadmium but there is not federal limit for it. Cadmium and lead are also found in children’s jewelry. This raises the question of what else is poisoning our kids, the painted items on the playground, not to mention the environmental impacts.
The University of Plymouth study also found that with long-term use, flakes of paint tend to come off of the glass and could be ingested by the drinker. Over time, that can create long-term exposure for the metals present. If the glass is used frequently, over several years, it’s the ideal condition for chronic exposure that even at low levels can pile up in the body. Studies show that chronic exposure of low levels may lead to kidney, bone and lung disease.
Lead in glass is more common than cadmium. If you’re concerned about lead in your dinnerware and glassware consider an at-home lead testing kit. The test is simple and it may save you and your family from daily toxic exposure. You can buy lead test kits for from online retailers. I recommend 3M Instant Lead Check Swabs.
SOURCES:
https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/wp-content/uploads/120/5/ehp.1104152.pdf
https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/1104431/
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/is-cadmium-as-dangerous-for-children-lead/
https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/cadmium/
https://www.osha.gov/SLTC/cadmium/healtheffects.html